1.2.6. Exercises¶
Note
We mean by function either FC or FB. Remember that an FC is a function without memory, it have only temporary variables.
An FB is a function with memory, it have static variables.
1.2.6.1. Line equation¶
Analog signal need to be scaled to a physical unit in order to be understood. Usually analog sensors and actuators are modeled as linear systems. Write a function that map the value of an analog signal to a physical one (or from physical signal to analog one). For example, to map voltage to temperature, or to map current to pressure value, or to map a speed to voltage.
1.2.6.2. Rising edge¶
Write a function the detect the transition of a signal from 0 to 1. This function have the same functioning of the standard one R_TRIG.
1.2.6.3. Falling Edge¶
Write a function the detect the transition of a signal from 1 to 0. This function have the same functioning of the standard one F_TRIG.
1.2.6.4. Retentive TON¶
Write a function that count the time if a signal is 1. If the signal go to zero the function should stop counting. If the signal return to one, the function should continue to count from the previous value. Refer to the following timing diagram.
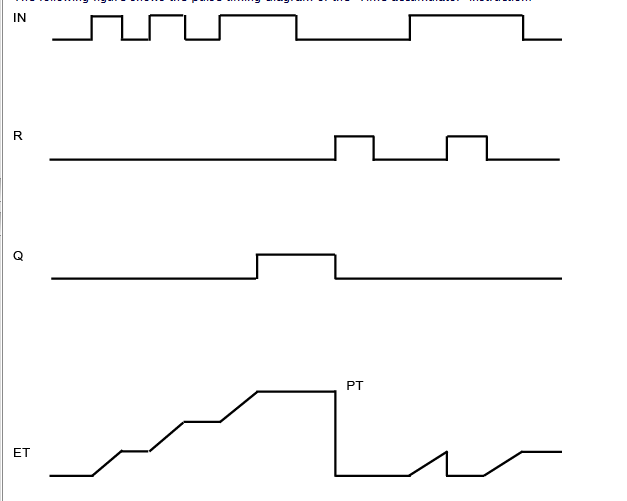
1.2.6.5. Blink¶
Write a function that toggle an output, with a determined frequency. The duty cycle of the signal can be tuned. Remember the duty cycle is the time (or percentage) of the time when the signal is high. In this exercise use time not percentage.
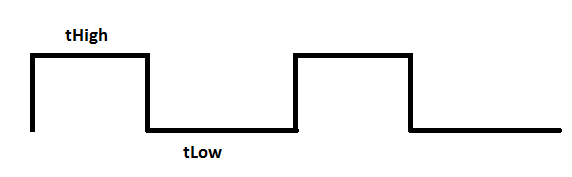
Preset times tHigh (on) and tLow (off) can be set as desired
1.2.6.6. Bi-stable cylinder¶
Write a function that control a cylinder. Imagine all digital input and outputs that are necessary to the correct functioning of the cylinder, as also any other signal or variable (not only physical input or output).
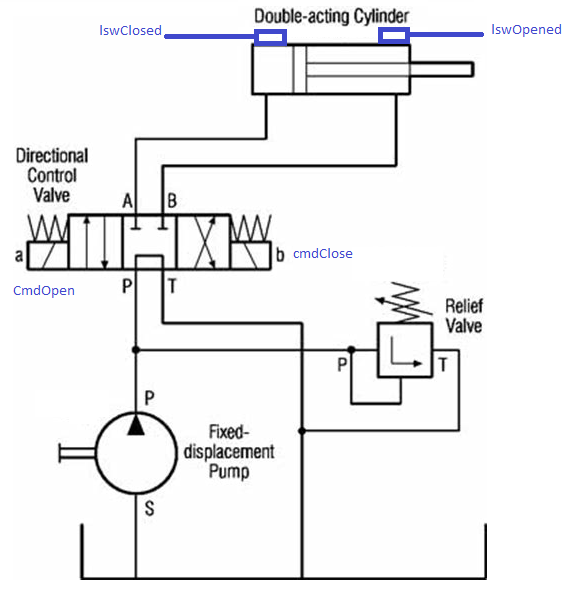
Double acting cylinder